Industrial automation is made possible with PLCs. PLCs are used in machinery, processes, and manufacturing systems; energy and transportation; and other industries. PLC programming is for freshers and engineering students who are new to the automation industry. PLC SCADA blog: Learn how it works, how to use it step by step, and why it plays a vital role in smart automation technology
PLC is Programmable Logic Controller.
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a rugged digital computer that humans manufacture for industrial surroundings. It looks at inputs and controls based on a pre-programmed logic and sends a control of outputs to train machines or the flow of procedures.
Key Features:
Robustness: Built to operate under severe conditions (dust, moisture, vibration, and so on). Real-time operation: Processes logic in real-time order to have accurate control. Modularity design: More input/output modules of PLC can expand it.
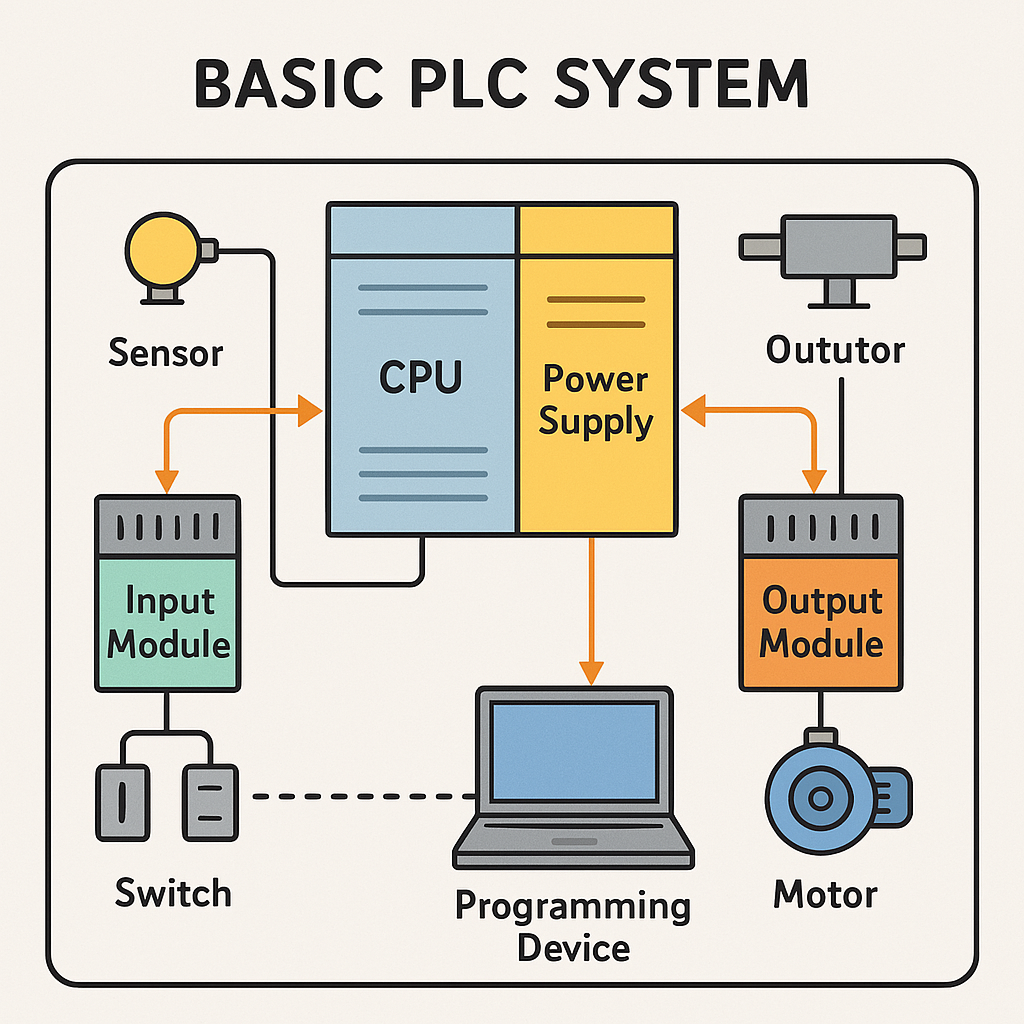
Simplified Elements of PLC System:
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
- The PLC brain.
- Performs control instructions within memory.
Power Supply
- Supplies energy to the PLC and PLC modules.
Input Modules
- Get signals of sensors, switches, etc.
- Put them in a form the CPU can understand.
Output Modules
- Send control commands to each actuators, motor, etc.
Programming Device
- A laptop or a handheld is used to communicate and program the control program into the PLC.
The Way PLCs Operate:
The process of a PLC occurs in an endless cycle referred to as a scan cycle:
- Input Scan: Scans the status of any input device.
2. Program Execution: The program forces the logic written by the user, depending on the input status.
3. Output: Changes output device status.
4. Housekeeping: Conducts in-house inspections and messages.
PLC Programming:
The design of PLCs is done by specialized languages that obey a standard IEC 61131-3. The most typical ones are
-
Ladder Logic (LD)
- Bears similarity to electrical relay logic diagrams.
- Simple enough to be read by electricians and technicians.
2. Function Block Diagram (FBD)
- Represents functions and connections by the use of blocks.
- It is suited for use in process control.
3. Structured Text (ST)
- Language with a high level, like Pascal.
- Applicable to highly sophisticated algorithms.
4. Quicksort IL (Instruction List) and SFC (Sequential Function Chart)
- Less popular but still advocated by a lot of PLCs.
Simple Ladder Logic:
Consider a system of the sort that a motor is expected to run on pressing a start button and should stop when a stop button is pushed.
|----[ Start ]----+----[/ Stop ]----( Motor )----|
|
+----( Latch )-------------------|- [ Start ]: Normally open push button.
- Stop ]: uninterrupted contact with the fail-safe push button.
- (Motor ): vehicle scadimento.
- (Latch ): causes the motor to continue running after the start button has been released.
Uses of PLCs:
The application of PLCs is a lot more diverse:
- Production: Assembly lines of factories, robotic manipulators.
- Power Plant control: Energy.
- Pump and valve control: Water treatment.
- Transport: Traffic light systems and railway automation.
- Building Automation: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning; elevated light control devices.
The benefits of the use of PLCs The benefits of using PLCs are as follows: a very rapid installation process very high degree of reliability
- Flexibility: Adapts very easily to other functions.
- Reliability
- Scalability: It is possible to expand it with other modules.
- Cost-effective: Eliminates the heavy wiring and relays.
Introduction to PLCs:
If you are excited to learn, take a close look at the guide below
- choosing a PLC brand: Siemens, Allen-Bradley, Mitsubishi, etc.
- Install the simulation program: There are numerous free software brands.
- Get familiar with ladder logic: use simple projects at first.
- Real hardware drills: Try to obtain a training kit.
- Search for free and paid courses as well as tutorials: Google offers a lot.
Recommended Resources:
- Books: “ Programmable Logic Controllers”” by ”Fran D. Petruzella
- Udemy, Coursera, and plc academy online Courses
- Simulation Software: LogixPro, TIA Portal, CX-Programmer
Wishing you very happy career growth!
